
New England Biolabs oferuje szeroki wybór rozwiązań do klonowań i mutagenezy, w tym zestaw do ukierunkowanej mutagenezy – Q5® Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit.
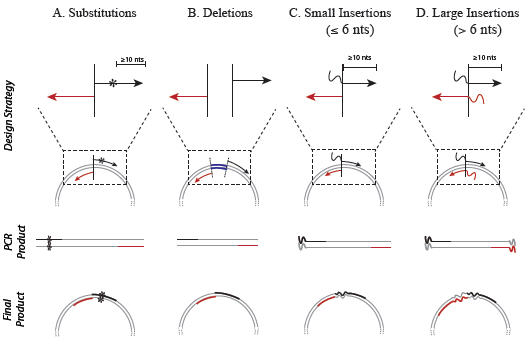
Zestaw jest wydajnym narzędziem, które pozwala na wprowadzanie mutacji punktowych, insercji lub delecji w czasie krótszym niż 2 godziny.
Zestaw jest dostępny z komórkami kompetentnymi lub bez.
-
Zastosowanie polimerazy wysokiej wierności gwarantuje wydajną i niezawodną amplifikację.
Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase jest 280 razy bardziej wierna, niż polimeraza Taq, co znacząco redukuje częstość błędów popełnianych podczas amplifikacji. -
Zastosowanie polimerazy typu HotStart umożliwia ustawienie reakcji w temperaturze pokojowej i zapobiega pojawieniu się niespecyficznych produktów amplifikacji.
-
Mieszanina enzymów KLD (Kinaza-Ligaza-DpnI) została zoptymalizowana dla maksymalnej wydajności reakcji.
-
Zestaw (#E0554) jest dostępny wraz z wysoce wydajnymi komórkami kompetentnymi NEB® 5-alpha Competent E. coli (High Efficiency)
-
Zestaw (#E0552) kompatybilny ze wszystkimi kompetentnymi szczepami E. coli.
-
Narzędzie NEBaseChanger™ pomaga w wygenerowaniu sekwencji starterów i ustawieniu reakcji PCR.
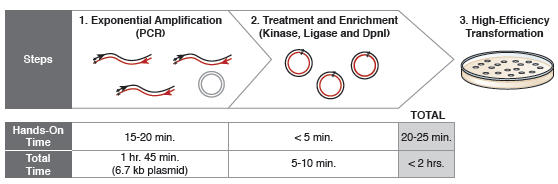
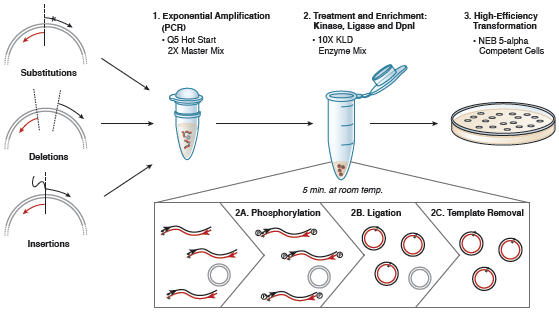
Ukierunkowaną mutagenezę przeprowadza się w oparciu o reakcję PCR, w której użyta jest polimeraza wysokiej wierności – Q5 Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase i odpowiednio zmodyfikowane oligonukleotydy (startery). Po reakcji PCR, zamplifikowany materiał jest bezpośrednio dodawany do unikalnej mieszanki enzymów Kinaza-Ligaza-DpnI (KLD) w celu szybkiej (5 minut) cyrkulizacji i usunięcia matrycy. Cała reakcja trwa niecałe dwie godziny. Uzyskanym kolistym plazmidem można transformować dowolne kompetentne komórki E. coli.
Narzędzie NEBaseChanger™ zostało opracowane, aby pomóc w wygenerowaniu sekwencji starterów i ustawieniu reakcji PCR
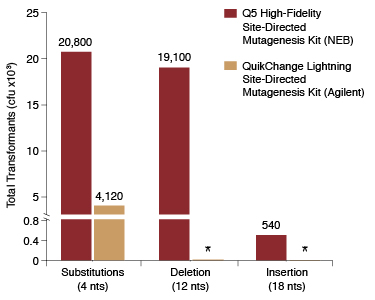
*Note that the QuikChange kit does not accommodate deletions and insertions of this size, so no comparison could be made for these experiments.

